-

Summary of basic knowledge of ultrasound(part four)
Section 9 Superficial Organ Ultrasonic Examination Measurement Methods and Normal Values Thyroid Ultrasound Measurement Methods (1) Thickness (anterior-posterior diameter) and width (left-right diameter) measurement of the thyroid gland 1. Standard measurement section: in a series of cross-sections of the thyroid gland, the thickest and widest part of the thyroid parenchyma is selected as the standard section, and the pressure of the probe should be as light as possible. 2. Measurement location: respectively selected at the edge of the hyperechoic line of the capsule at the thickest and widest parts of the thyroid gland. 3. Normal adult reference value (cm): the thickness of the left and right leaves is 1.5~2.0cm, The width is 2.0~2.5cm, and the thickness of the isthmus is less than 0.5cm. (2) Measurement of the long diameter (upper and lower diameter) of the thyroid gland 1. Standard measurement section: In a series of longitudinal sections of the thyroid gland, the longest part of the thyroid parenchyma is selected as the standard section, and the pressure of the probe should be as light as possible. 2. Measurement locations: respectively selected on the edge of the hyperechoic line of the capsule at the longest part of the thyroid gland. 3....
-

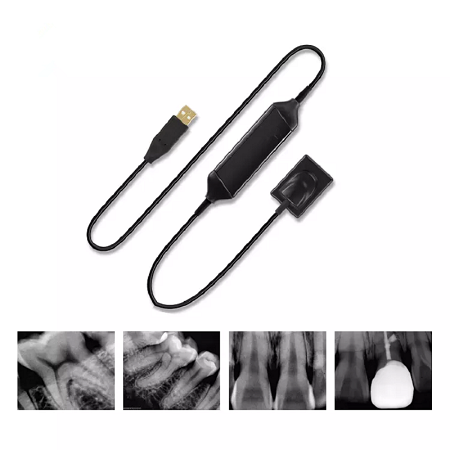
The Working Principle Of RVG Sensor
X-rays were invented 122 years ago by WH Roentgen. These have found various applications, such as in manufacturing, medical imaging and other fields. X-rays also play a vital role in the dental field. The dentist takes radiographs to understand the damage to the tissue under the gem. With the advancement of technology, dental imaging technology has also made great progress. Digital radiography was introduced into the dental field by French dentist DR. Francis Moyen, 1987. Seeing the effectiveness of this technology, various changes have been made, and new systems are being developed to implement this technology. Digital radiography is also called RadioVisioGraphy. The RVG sensor is used for digital radiography. The working principle of RVG sensor The sensor has two sides: reactive power and reactive power. The reaction side should be used to capture images. The tissue is exposed to X-ray radiation, and the refracted light is captured by the sensor. Process the image immediately and convert it to digital data using an analog-to-digital converter. These digital data are sent to the computer, where the doctor can immediately view the scan results. The cable attachment is located at the invalid end of the sensor. When the non-reactive surface is exposed...
-

Summary of basic knowledge of ultrasound(part three)
Section 7 Measurement methods and normal values of gynecological ultrasonography one. Uterus Three diameters need to be measured, the longitudinal diameter, transverse diameter and anteroposterior diameter of the uterus. 1. Uterine longitudinal diameter (upper and lower diameter) measurement; (1) Measurement section: Sagittal section of the uterus. It is necessary to clearly show the symmetrical sections from the fundus of the uterus to the internal os of the cervix, the muscle layer, and the front and back layers of the endometrium. (2) Measurement location: Uterine body: the distance between the outer edge of the uterine fundus and the internal os of the cervix. Cervix: the distance between the internal os of the cervix and the external os of the cervix. (3) Normal value: palace body 5.0 ± 1.0cm. Cervix 2.5-3.0cm. 2. Measurement of the transverse diameter (left and right diameter) of the uterus: (1) Measurement section: coronal section of the uterus. The uterus needs to be transected, and the measurement is performed at the middle of the uterine body and when the image shows the largest elliptical section (not at the place where the image is triangular). (2) Measurement position: the maximum left and right diameter passing through the uterine body....
-

suomali
-

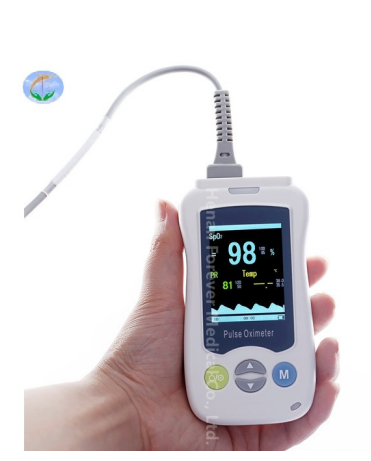
What Is The Important Role Of Oximetry in COVID-19?
With the increasing emphasis on health, the demand for oximeters is gradually increasing, especially after the COVID-19, the demand for oximeters is exponentially more widespread! So what is so unique about this little oximeter and what important role does it play in the fight against the new epidemic in this smokeless battlefield? What is an oximeter? An oximeter, also known as a pulse oximeter, is a device that monitors the oxygen content of blood in the body in real time without the need for blood sampling, through a detector or sensor. It is a small medical device that measures the body’s oxygen saturation, pulse rate and perfusion index. The oxygen saturation of a normal person is between 94% and 100%, below 90% needs to be taken seriously. COVID-19 can lead to lung infections which can lower blood oxygen levels. When blood oxygen levels are at a low level, one may feel fatigue and shortness of breath, even without any discomfort, but such a situation can be dangerous. Oximetry is one of the clinical diagnostic methods for neocoronary pneumonia. Changes in blood oxygen levels can be used to determine if you have neocoronary pneumonia, and for some mild cases of neocoronary...
-
Summary of basic knowledge of ultrasound(part two)
Section 3 Ultrasound examination of the pancreas and its normal values At present, there is no uniform standard for the ultrasound measurement of normal pancreas, and most authors use the thickness (anterior-posterior diameter) of the pancreas as the standard. specific method: one. Pancreatic head measurement 1. Select a facet. Long-axis section of the pancreas, showing the head of the pancreas clearly; 2. Measurement site: measured in front of the inferior vena cava, measurement generally does not include the uncinate process 3. Normal reference value (adult): ≤2.5cm two. Pancreatic body measurement ! . Select the slice: long-axis slice of the pancreas to show the body of the pancreas clearly: 2. Measurement site: Measure in the vertical line in front of the abdominal aorta. 3. Normal reference value (adult): ≤2.0cm three. Measurement of pancreatic tail 1. Select the section: long-axis section of the pancreas to clearly show the tail of the pancreas: 2 Measurement site: measure at the left edge of the abdominal aorta or the left edge of the spine; 3. Normal reference value (adult): ≤2.0cm Section IV Renal ultrasonography measurement methods and normal values one. Kidney length (upper and lower diameter) measurement 1. Measurement plane: Coronal or sagittal longest plane...
If you have any question, please contact us